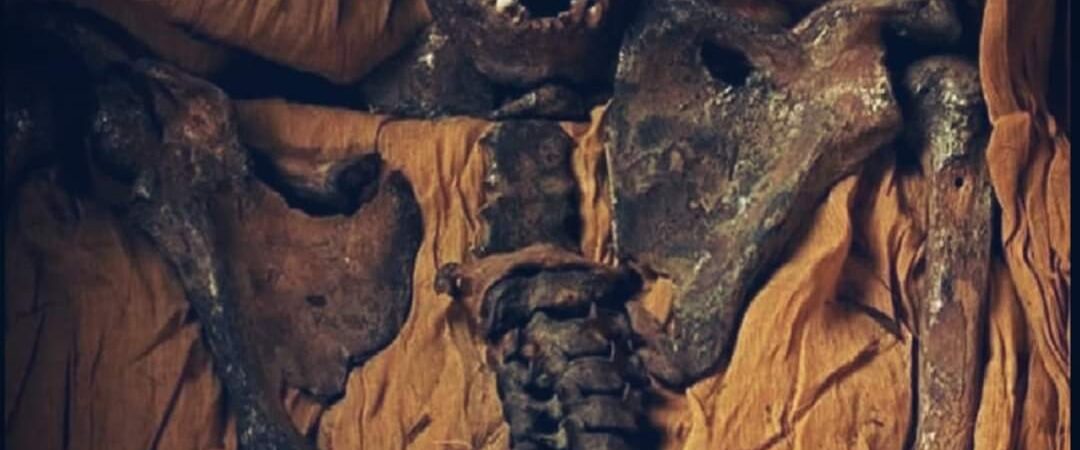
The discovery of the skeleton initially thought to belong to Akhenaten in 1907 provides a fascinating glimpse into the complex history of ancient Egyptian royalty and the challenges of archaeological research. This skeletal find, accompanied by a sarcophagus inscribed with royal epithets, sparked significant debate among scholars about the identity of the remains and the tumultuous period of Akhenaten’s reign.
Historical Context and Discovery

1. Initial Discovery:
Year and Location: The skeleton was uncovered in 1907 during archaeological excavations in Egypt. The sarcophagus in which it was found was inscribed with epithets suggesting it belonged to a significant royal figure. This led researchers to initially conclude that the remains were those of Akhenaten, the Pharaoh known for his radical religious reforms.
2. Identification Challenges:
Historical Background: Akhenaten, who ruled Egypt during the 18th Dynasty (circa 1353-1336 BCE), is remembered for his controversial religious reforms that introduced the worship of Aten, a single sun disk deity, diverging from the traditional polytheistic practices. His reign was marked by profound cultural and religious changes, which were subsequently reversed by his successors. Akhenaten’s death and the fate of his mummy have been subjects of considerable debate due to the upheaval and subsequent attempts to protect royal remains from tomb robbers.
Movement of Mummies: The history of Egyptian mummies is complicated by the frequent relocation of royal remains to safeguard them from grave robbers. This often resulted in mummies being placed in coffins or tombs that did not originally belong to them, adding layers of confusion for modern archaeologists.
Modern Analysis and Findings
1. DNA Testing:
Recent Developments: Advances in DNA testing have played a crucial role in confirming the identity of the skeleton. Despite the poor preservation of the remains, genetic analysis has been able to establish a match with the lineage of Akhenaten. This scientific confirmation aligns with the historical evidence suggesting the skeleton’s identity as Akhenaten, resolving a long-standing question about the Pharaoh’s final resting place.
2. Significance of Akhenaten:
Religious and Cultural Impact: Akhenaten’s reign is notable for its dramatic shift in religious practice. His promotion of Aten worship represented a significant departure from Egypt’s traditional pantheon, which included gods such as Amun-Ra, Osiris, and Horus. This religious revolution was short-lived, as his successors, notably Tutankhamun and Ay, reinstated the old gods and rejected Akhenaten’s reforms.
Artistic and Architectural Legacy: The period of Akhenaten’s rule, known as the Amarna Period, also saw changes in art and architecture, with depictions of the royal family in more naturalistic and informal poses, contrasting with the formal and idealized representations of previous dynasties.
Archaeological and Historical Implications
1. Insights into Ancient Egyptian Royalty:
Tomb Robbing and Preservation: The discovery highlights the challenges faced by archaeologists in deciphering the true identities of royal mummies. The practice of moving mummies and the subsequent mix-ups in tombs provide insight into the lengths to which ancient Egyptians went to protect their dead from theft and desecration.
Historical Understanding: Confirming Akhenaten’s identity contributes to a better understanding of the historical narrative of the 18th Dynasty, shedding light on the religious and political shifts of the time. It also underscores the importance of combining archaeological, historical, and scientific methods to piece together the lives of ancient figures.
2. Public and Academic Interest:
Cultural Impact: The confirmation of Akhenaten’s identity has significant implications for both scholars and the public. It provides a clearer picture of the controversial Pharaoh’s life and legacy, contributing to the broader understanding of ancient Egyptian history and its impact on subsequent generations.
Ongoing Research: The case of Akhenaten exemplifies the broader challenges and successes in the field of Egyptology. It serves as a reminder of the complexities involved in studying ancient civilizations and the ways in which modern technology can aid in unraveling historical mysteries.
In summary, the 2007 confirmation of the skeleton’s identity as Akhenaten brings closure to a long-standing debate and provides valuable insights into one of ancient Egypt’s most revolutionary rulers. The combination of historical records, archaeological evidence, and modern scientific techniques has enabled a more accurate reconstruction of the life and legacy of Akhenaten, offering a deeper understanding of this enigmatic Pharaoh’s place in history.